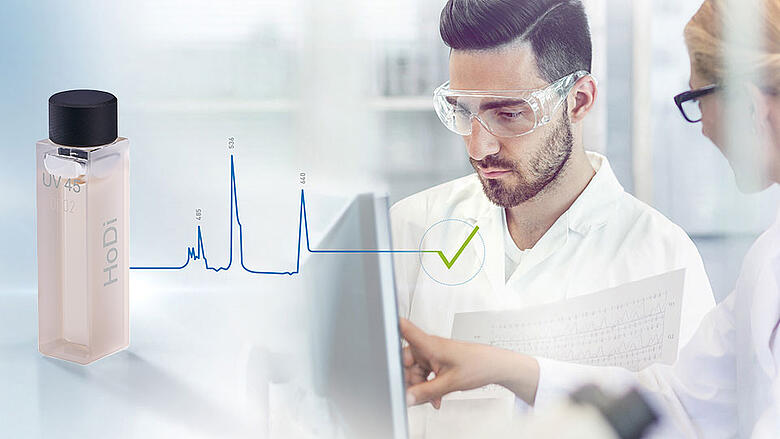
Welcome to Hellma. The world of highest precision!
Hellma is independent provider of integrated solutions for optical analysis and leading manufacturer of high-precision products made of optical glass, quartzglass and crystals. Photonics and molecular spectroscopy customers around the world appreciate Hellma products for their exceptional quality and reliability.

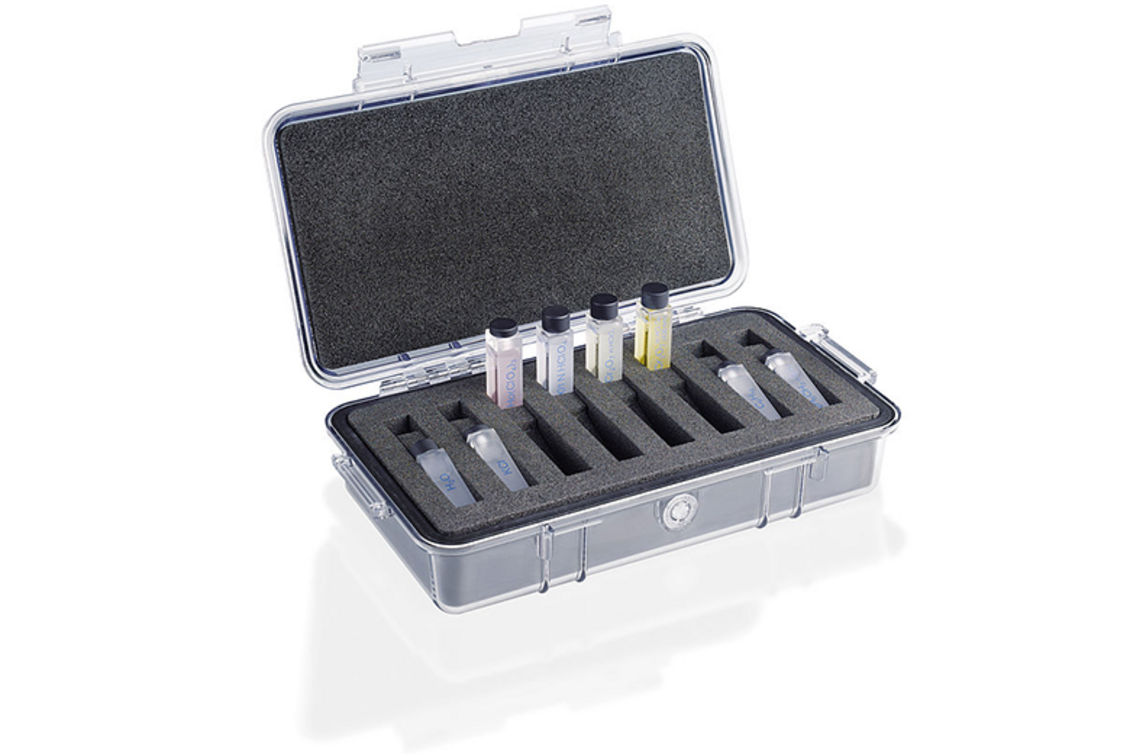
Laboratory Products
Cuvettes, UV/Vis reference materials, micro volume measurement cells, immersion probes, OEM
continue
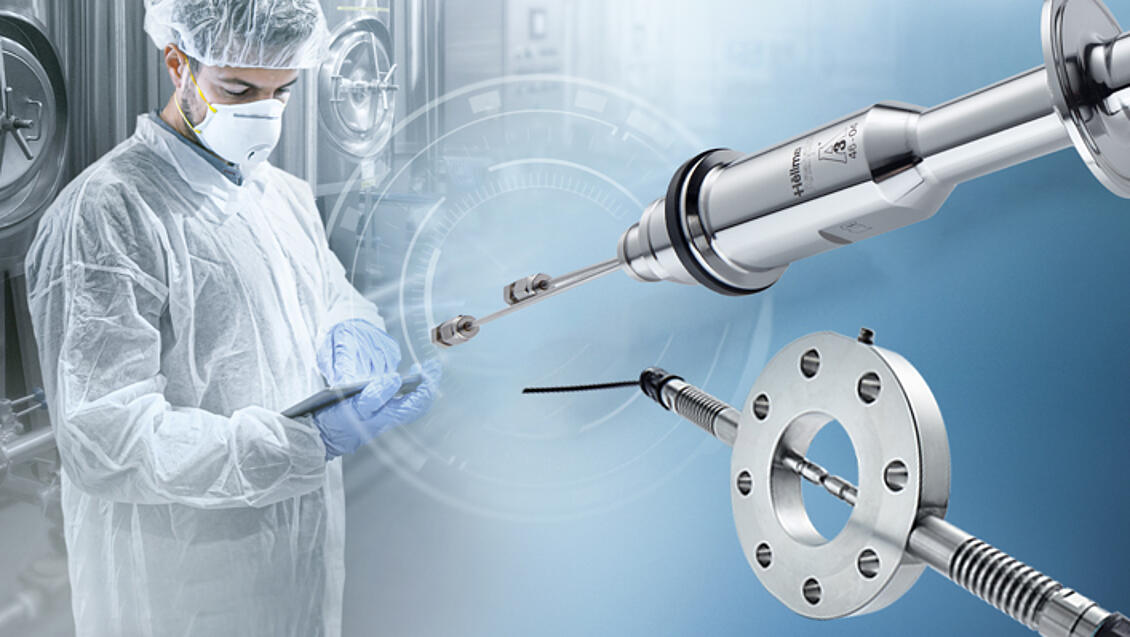
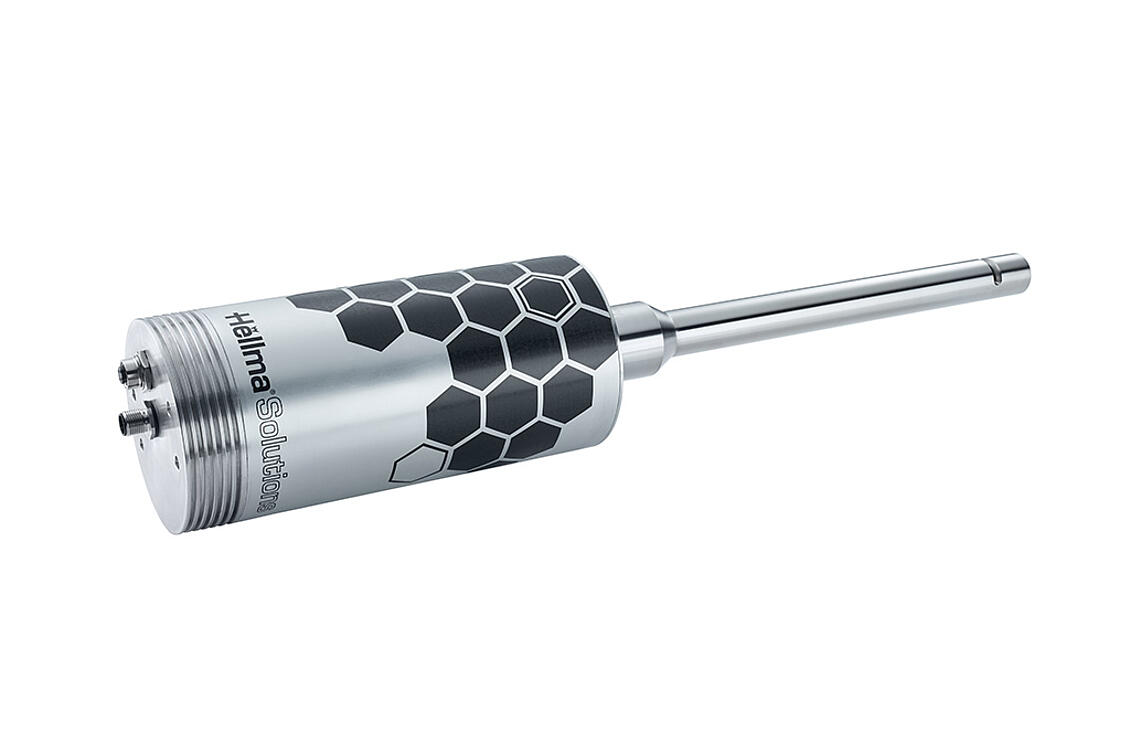
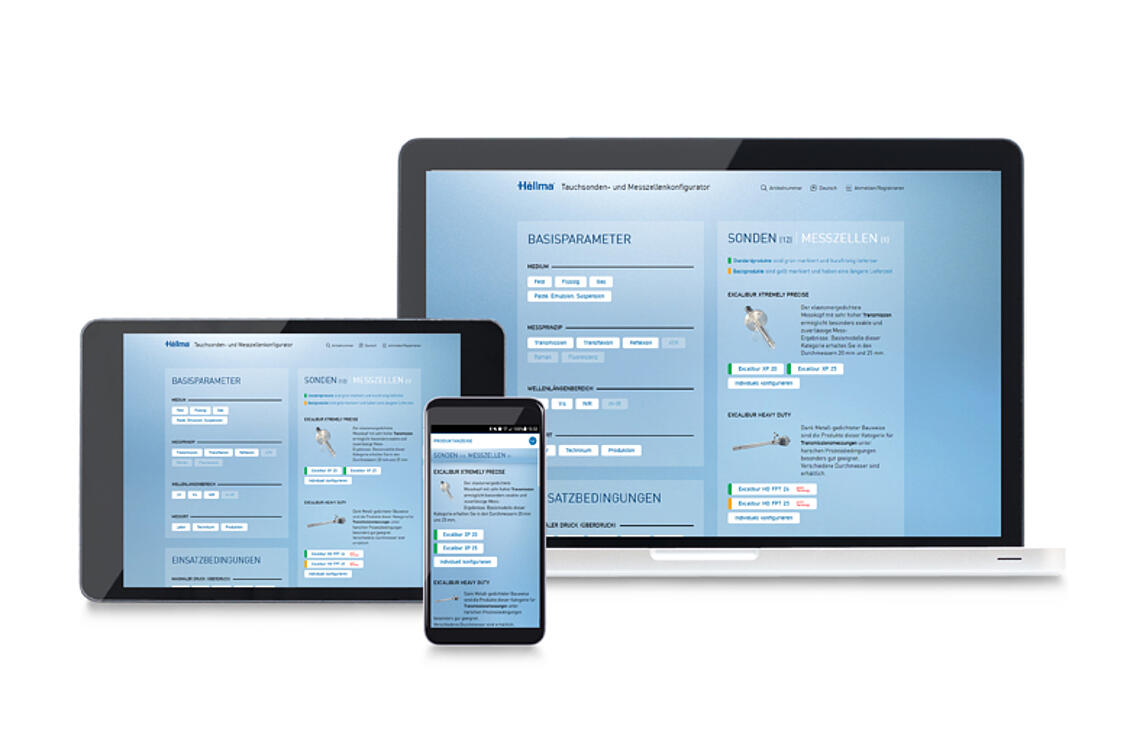
Process Analytics
The world's largest product portfolio of optical probes and measurement cells - standard products and product configurator
continue
Calibration Laboratory
Recalibration of UV/Vis reference materials based on DIN EN ISO 17025 with calibration certificate
continueVideos
Webinar: Vibrational Spectroscopy and NIR Technology for Polymer Sorting (EN)
European Pharmacopoeia EP 10 | How to comply with the new requirements
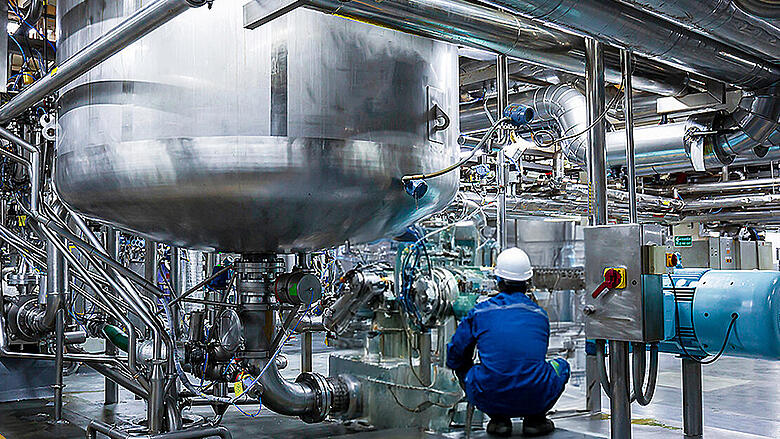

polyol production
Online Monitoring of Product-Relevant Parameters in the Production of Polyols

Solvent Receycling
Endpoint Determination of a Distillation Process using NIR Spectroscopy in the Recovery of Solvents
continue
Natural Gas Analysis
Qualitative Analysis of the Composition of Natural Gas Using Raman Spectroscopy
continue