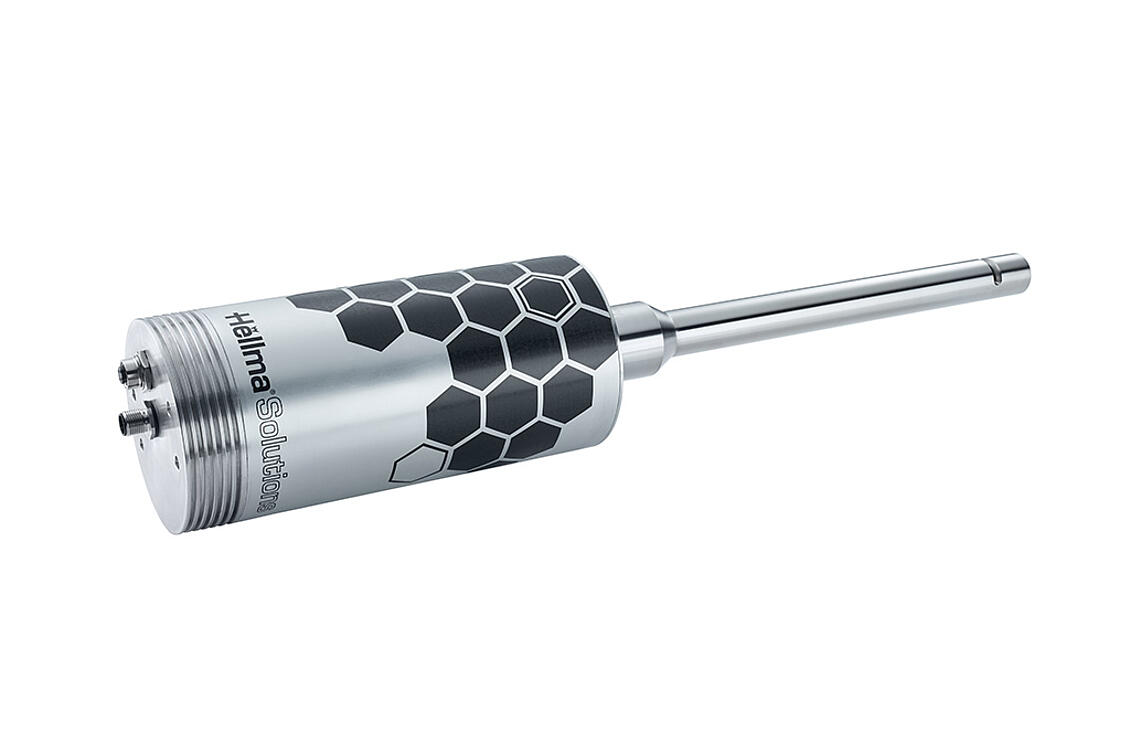
Calibration Standards
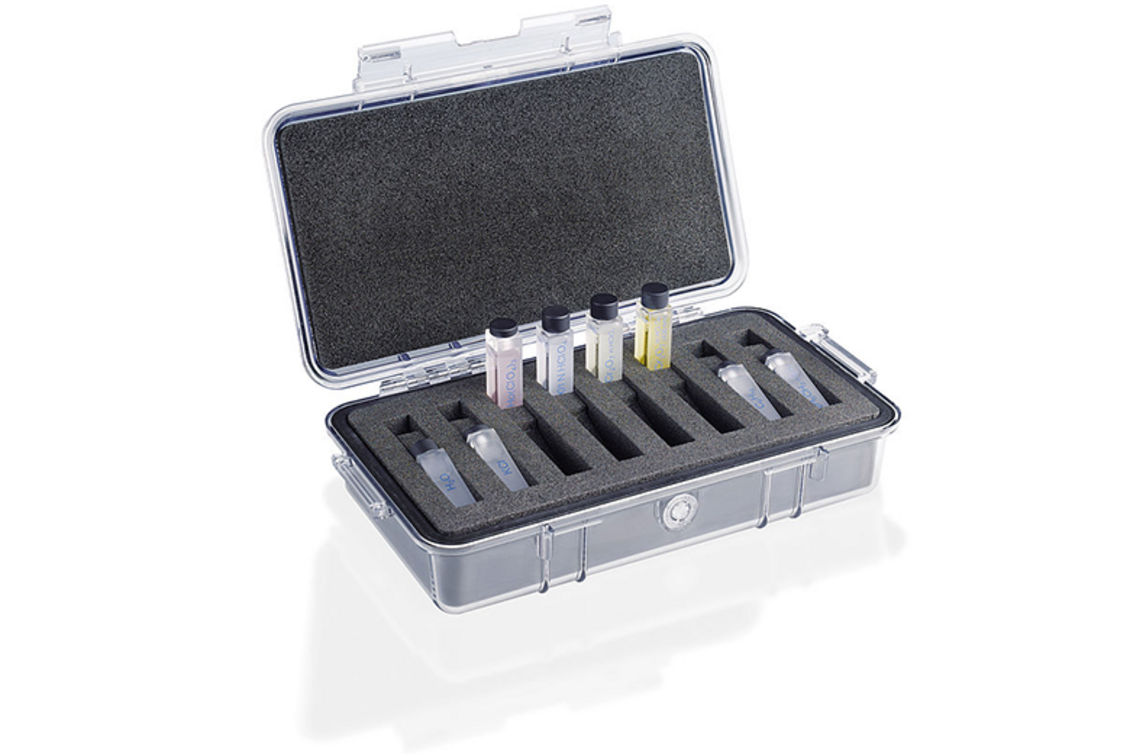


Reliable measurement results through regular verification of the spectrometer using certified reference materials